The Garfield Thomas Water Tunnel is a unique experimental facility for hydrodynamic research and testing. The 48-inch (1.2-meter) diameter water tunnel enables the research staff to conduct basic and applied investigations in the fields of cavitation, hydroacoustics, turbulence, transition, hydrodynamic drag, and hydraulic and subsonic turbomachinery. Instrumentation and testing methods have been developed to study noise, vibration, vehicle dynamics, and the interaction between the propulsor and vehicle body.
Drag
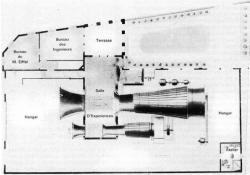
Late in life, the renowned structural engineer Gustave Eiffel (1832-1923) embarked on aeronautical research. Reliable data and repeatable research methods were rare in the early 1900s, but Eiffel brought an engineer's discipline to the field. In the process, he produced the most accurate aeronautical data of the time, confirmed a long-held theory about fluid flow that had never been unequivocally proven, and established a laboratory that became a model for future practice.
Innovations

Late in life, the renowned structural engineer Gustave Eiffel (1832-1923) embarked on aeronautical research. Reliable data and repeatable research methods were rare in the early 1900s, but Eiffel brought an engineer's discipline to the field. In the process, he produced the most accurate…
Read MoreThe Garfield Thomas Water Tunnel is a unique experimental facility for hydrodynamic research and testing. The 48-inch (1.2-meter) diameter water tunnel enables the research staff to conduct basic and applied investigations in the fields of cavitation, hydroacoustics, turbulence, transition,…
Read More

