Slow Moving Vehicle (SMV) Emblem Makes Significant Contributions To Agricultural And Highway Safety Worldwide. 1961- 63 Developed By Kenneth A. Harkness, Department Of Agricultural Engineering On The Ohio State University Campus. 1964 Became An ASAE Standard 1968 Specified In National Uniform Vehicle Code 1971 First Asabe Standard Ratified By American National Standards Institute (ANSI). Became Occupation Safety And Health Act (OSHA) Regulation. Ohio Farm And Home Safety Committee Provided Leadership
In Achieving Acceptance Dedicated 1992
OH


A Crucial Step In The Evolution Of Modern Animal Agriculture Was The Development Of Mechanical Ventilation Methods For Animal Housing. Air Inlets Are Pivotal To Good Ventilation. In 1948 William F. Millier, Working At Cornell University Under The Direction Of Professor Clesson Turner, Tested And Published The Concept Of The Slotted Inlet. Professor Turner And Others At Cornell University Subsequently Continued To Develop Slotted Inlet Systems And Systematize Design Methods.
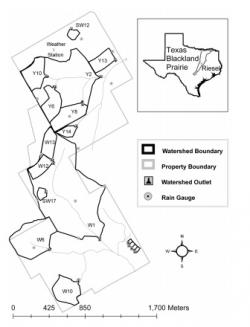
In the mid 1930's, the USDA Soil Conservation Service (SCS) realized the importance of hydrologic processes on agricultural fields and watersheds and determining their impact on soil erosion, floods, water resources, and the agricultural economy. In response, the SCS Hydrologic Division established experimental watersheds in Coshocton, Ohio, Hastings, Nebraska, and Riesel, Texas, and operated them until 1954 when the watersheds were transferred to the newly created Agricultural Research Service (ARS).
ARS Grassland, Soil and Water Research Laboratory near Riesel, Texas.

The first laser grade control was developed by agricultural engineers James Fouss and Norman Fausey of USDA's Agricultural Research Service at The Ohio State University in the mid-1960's. That system controlled the precise depth and grade of subsurface drains by regulating trenching and plow-type drainage machines. Photo cells mounted on the drainage machine automatically raised and lowered the digging device, keeping the cells centered on a laser beam set to the desired elevation and grade.
matic grade‐control system on the plow.
In 1926, Ives Hall, the original Agricultural Engineering Building at The Ohio State University, Columbus, was designated as ASAE's first engineering landmark in honor of department founder and 18th president of ASAE Fredrick Walter Ives. Frederick W. Ives 1884 - 1924.
Ives Hall was on the corner of Neil and Woodruff Avenues from 1926 - 2002. This display has been constructed with brick from the original structure.
The Cincinnati Observatory, “The Birthplace of American Astronomy,” is the oldest professional observatory in the United States. Ormsby MacKnight Mitchel, the “Father of American Astronomy,” founded the observatory in 1842. John Quincy Adams laid the cornerstone for the observatory on Mt. Ida, later renamed Mt. Adams. The original Merz und Mahler 11-inch refractor telescope was put into service in 1845 and is still in use here today on Mount Lookout.

Lunken Field, now also known as Cincinnati Municipal Lunken Airport, opened in 1925 on ground purchased from the Cincinnati Polo Club. The nation’s largest municipal airport at the time, it attracted several aerospace enterprises, starting with early aviator J. Richard “Dixie” Davis, who established his barnstorming enterprise there in 1925. In 1928, several other firms established enterprises at the field – each making history.

On this 84-acre meadow in 1904 and 1905, the Wright Brothers successfully mastered the mechanics of controlled, powered, heavier-than-air flight. The brothers also built the world’s first airport here, and in 1910 the Wright Company School of Aviation established a flying school on the site and trained many of the world’s first pilots, including some of the first military pilots, such as Thomas DeWitt Milling.

DayGlo fluorescent pigments, a new class of pigments based on fluorescent dyes and polymeric materials, were developed between the 1930s and 1950s by scientists at Switzer Brothers, Inc. (now Day-Glo Color Corp.). These pigments absorb various light frequencies (visible and invisible to the human eye) and reemit them, producing intense visible colors that appear to glow, even in daylight.

The Chemical Abstracts Service, a division of the American Chemical Society, has provided the most comprehensive repository of research in chemistry and related sciences for over 100 years. CAS innovations have fueled chemical research through development of the CAS RegistrySM and CAS databases which contain invaluable information for chemical scientists, including SciFinder® and STN®.
Innovations

In his laboratory at Western Reserve University (Now Case Western Reserve University), Edward W. Morley carried out his research on the atomic weight of oxygen that provided a new standard to the science of chemistry. The accuracy of his analyses has never been superseded by chemical means. His…
Read More
Most of the locks were 184 feet long and 36 feet wide, able to handle boats up to 160 feet long. The sandstone locks (along with wood miter gates, rock-filled timber-crib dams and bypass canals with guard gates) created a slackwater navigation system stretching over 90 miles.
…

The Miami Conservancy District flood control project was the direct result of the disastrous flood of 1913, when waters from the Miami, Stillwater, and Mad rivers flooded Dayton and surrounding communities in the Miami Valley. More than 400 lives were lost and property damage exceeded $100…
Read More
This 50,000-ton die-forging press is among the largest fabrication tools in the world. It was designed and built for the U.S. Air Force by the Mesta Machine Company of Pittsburgh, following the discovery of a 30,000-ton press used by the Germans in World War II (later acquired by the Soviet…
Read More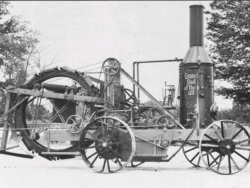
During the post-Civil War era, efforts to cultivate the land for higher crop yields resulted in the digging of thousands of miles of ditches to improve land drainage. Accurately graded ditches were needed for open drainage, pipeline trenches and placement of underground agricultural drainage…
Read More
The Cincinnati Observatory, founded by Ormsby MacKnight Mitchel in 1842, is America’s oldest public/professional observatory. The observatory was situated on Mt. Adams, east of the current downtown Cincinnati; the hill was named for former President John Quincy Adams when he laid the observatory…
Read More
Constructed on 1,040 acres just 10 miles southwest of the city center, the Cleveland Hopkins Airport was the first major airport in the world to provide an integrated system of paved landing surfaces, lighted runways, and a terminal complex consisting of hangars and operating facilities.…
Read More
"This is the first Portland cement concrete street built in the United States ... Here started the better roads movement which has given our citizens from coast to coast swift and sure transportation."
- Historic marker, Bellefontaine, Ohio, celebrating the 50th anniversary of…

This compressor was a product of the combined technology and design heritage of both the C. & G. Cooper Company of Mount Vernon and the Bessemer Gas Engine Company of Pennsylvania, which had merged in 1929. Ralph L. Boyer, the chief architect of the GMV, worked for Cooper-Bessemer from 1926…
Read More
These engines, built by Cooper & Co., of Mount Vernon are among the oldest surviving agricultural steam engines to show the evolution from the portable, skid-mounted engine (ca. 1860) to the horse-drawn engine (1875), through the self-propelled but horse-guided engine (1875) and finally to…
Read More
Wind dynamics were a major consideration in building such a huge structure. When winds blow against the building, they are deflected up over the roof, creating a partial vacuum that can draw the roof up with a force several times greater than the direct force of the wind. Wind tunnel testing on…
Read More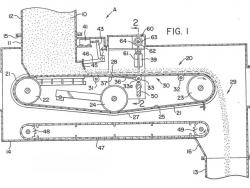
A variety of mechanical feeders, including drag-chain conveyors and rotary pocket feeders, historically have been used to volumetrically control the flow of fuel to coal pulverizers on power generators. Most power generation in the United States has relied on burning fossil fuels in steam…
Read More
In operation since 1944, the Icing Research Tunnel is the oldest and largest refrigerated icing wind tunnel in the world. Technology developed there enables aircraft to fly safely through icing clouds. Two firsts include the unique heat exchanger and the spray system that simulates a natural…
Read More
The 16-story Ingalls Building, still in use today, was the world's first reinforced concrete skyscraper. Its success led to the acceptance of high-rise concrete construction in the United States.
Melville E. Ingalls, for whom the building is named, spent two years convincing city…
Read More
Although not the first four-wheel-drive vehicle or the first designed for rough, multipurpose field use, the Jeep MB was built as an unusual combination of these and other features of modern vehicle design in the World War II era.
The prototype four-cylinder "Quad" was designed in 1940-…
Read More
In 1866, the Covington and Cincinnati Suspension Bridge was the largest suspension bridge in the world. Also called the Ohio Bridge, it was officially renamed the John A. Roebling Bridge in 1983. It was the first permanent bridge over the Ohio River and the only public project in America…
Read More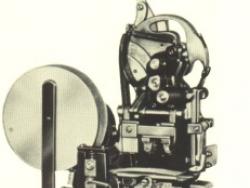
This was the first successful machine for mechanizing the identification and price marking of retail merchandise. At a single stroke of the operating handle, the machine formed a tag from a roll of stock, imprinted it with price and other information, formed a wire staple, and stapled the tag to…
Read More
The 1905 Wright Flyer III, built by Wilbur (1867-1912) and Orville (1871-1948) Wright, was the world's first airplane capable of sustained, maneuverable flight. Similar in design to their celebrated first airplane, this machine featured a stronger structure, a larger engine turning new "bent-end…
Read More
The convenient dry-copying process for printed pages is among the truly revolutionary inventions of the century. In 1937 Chester Carlson, a New York patent attorney, developed the concept of applying an electrostatic charge on a plate coated with a photoconductive material. On November 22, 1938…
Read More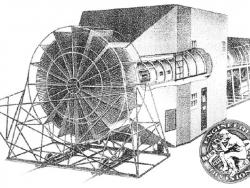
Wind tunnel testing of aircraft models is essential to determine aerodynamic parameters such as lift and drag. The 5-foot Wright Field wind tunnel is an early example of the modern wind tunnel, well known from the early 1920s to the late 1950s for its contributions to research and the…
Read More

