Air Force


BinghamtonState: NYZip: 13905Country: USAWebsite: https://www.asme.org/about-asme/who-we-are/engineering-history/landmarks/210-link-c-3-flight-trainerCreator: Link, Edwin
During the 1920s, Edwin A. Link was employed in his father's organ building and repair business. He obtained his pilot's license in 1927 and became convinced that a mechanical device could be built as an inexpensive method to teach basic piloting. Link received three patents on his flight trainer (No. 1,825,462, March 12, 1930; No. 2,244,464, June 3, 1941; and No. 2,358,016, Sept. 12, 1944).

Wind tunnel testing of aircraft models is essential to determine aerodynamic parameters such as lift and drag. The 5-foot Wright Field wind tunnel is an early example of the modern wind tunnel, well known from the early 1920s to the late 1950s for its contributions to research and the development of nearly every major aircraft and associated hardware used by the US Air Force and its predecessor, the Army Air Service.

Getafe Airfield was the site of the world’s first successful rotorcraft flight, on January 17, 1923. Lieutenant Alejandro Gómez Spencer piloted a C.4 Autogiro designed and built by Juan de la Cierva, who tested a series of autogiros between 1920 and 1924 at the Getafe site. Cierva’s autogiros introduced important technologies and flight techniques that led to the development of helicopters and other rotary wing aircraft. Getafe Air Base, established in 1911, now houses several training and transport units of the Spanish Air Force, as well as two aerospace manufacturing plants.

Established in 1935 as the Valparaiso Bombing and Gunnery Base, the base supported the U.S. Army Air Corps, the predecessor to the U.S. Air Force, as its primary facility for training new pilots in bombing and gunnery tactics. It also served as a test facility for aircraft, aircraft armament, air-delivered munitions and other aircraft systems. The base was renamed Eglin Field in 1937 in honor of Air Corps aviator Lt. Col. Frederick I. Eglin, who trained pilots during World War I, and who had recently died in an aircraft accident. After Congress created the U.S.

Innovations


Established in 1935 as the Valparaiso Bombing and Gunnery Base, the base supported the U.S. Army Air Corps, the predecessor to the U.S. Air Force, as its primary facility for training new pilots in bombing and gunnery tactics. It also served as a test facility for aircraft, aircraft armament,…
Read More
Getafe Airfield was the site of the world’s first successful rotorcraft flight, on January 17, 1923. Lieutenant Alejandro Gómez Spencer piloted a C.4 Autogiro designed and built by Juan de la Cierva, who tested a series of autogiros between 1920 and 1924 at the Getafe site. Cierva’s autogiros…
Read More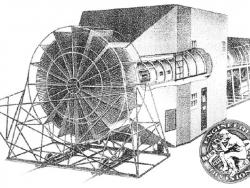
Wind tunnel testing of aircraft models is essential to determine aerodynamic parameters such as lift and drag. The 5-foot Wright Field wind tunnel is an early example of the modern wind tunnel, well known from the early 1920s to the late 1950s for its contributions to research and the…
Read More
During the 1920s, Edwin A. Link was employed in his father's organ building and repair business. He obtained his pilot's license in 1927 and became convinced that a mechanical device could be built as an inexpensive method to teach basic piloting. Link received three patents on his flight…
Read More


