On 4 June 1783, Joseph Michel and Jacques Etienne Montgolfier captured the imagination of the world with their first balloon flight at Cordeliers Square. There were no passengers, but the Regional Council and the whole town population saw the machine go up and stay aloft at 500 meters for ten minutes. The scientific world raced to make use of the Montgolfiers’ discovery, and all accomplishments made since then by aeronauts, aviators, and astronauts can be traced directly to this site.
Frontiers of Knowledge

T.S.C. Lowe’s Observation Flight
On this site, which was the Dutch Flats Airport, Charles A. Lindbergh made the first flight of his Spirit of St. Louis airplane, constructed in 60 days by dedicated employees of Ryan Airlines, Inc. The 20-minute flight on 28 April 1927 was witnessed by those who built the aircraft. Lindbergh describes the flight:

The first company in the United States dedicated solely to the production of the liquid rocket engine, Reaction Motors, Inc. (RMI) was formed in 1941. Its four founders were rocket enthusiasts and members of the American Rocket Society. RMI developed the rocket motors that powered the first supersonic flight, that of the X-1; the retro rockets for five NASA surveyor lunar soft landers; and prepackaged liquid rocket engines for the U.S. Navy Bullpup A & B air to ground missiles, among many other pioneering programs.

Born 20 July 1873 in the state of Sao Paolo, Alberto Santos Dumont moved to Paris in 1891 but never forgot his birthplace. He soon began experimenting with flying, and designed his first balloon, the Brasil, in 1898. He later built and flew 11 dirigibles, including the prize-winning Number 6. He flew his first airplane, the 14 bis, on 23 October 1906, the first aircraft to take off and land without any external assistance. His many other contributions to aviation included his 1909 Demoiselle, the precursor to modern light airplanes.

Izaak Maurits Kolthoff (1894–1993) has been described as the father of modern analytical chemistry for his research and teaching that transformed the ways by which scientists separate, identify, and quantify chemical substances. Once a collection of empirical recipes and prescriptions, the field of analytical chemistry is today an essential branch of chemistry built upon solid theoretical principles and experimental techniques, the basis of which was formed over the course of Kolthoff’s nearly 80-year career.
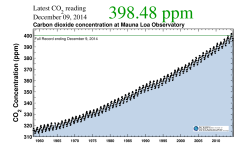
Charles David Keeling of Scripps Institution of Oceanography was the leading authority in establishing the global atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) record. In 1958, Keeling began measuring atmospheric CO2 concentrations from Hawaii’s Mauna Loa Observatory. Using rigorous analytical procedures, he revealed new information about natural and man-caused carbon trends.

In the years 1926 to 1956, the German chemist Hermann Staudinger carried out his pathbreaking research on macromolecular chemistry in Freiburg. His theories on the polymer structures of fibers and plastics and his later research on biological macromolecules formed the basis for countless modern developments in the fields of materials science and biosciences and supported the rapid growth of the plastics industry. For his work in the field of polymers, Staudinger was awarded the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 1953.

In 1900, Moses Gomberg, Professor of Chemistry at the University of Michigan, confirmed the existence of a stable, trivalent organic free radical: triphenylmethyl. In so doing, he challenged the then prevailing belief that carbon could have only four chemical bonds. Gomberg’s discovery made a major contribution to theoretical organic chemistry and fostered a field of research that continues to grow and expand. Today, organic free radicals are widely used in plastics and rubber manufacture, as well as medicine, agriculture and biochemistry.
Innovations
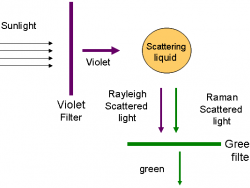
"I propose this evening to speak to you on a new kind of radiation or light emission from atoms and molecules." With these prophetic words, Professor C. V. Raman of Calcutta University began his lecture to the South Indian Science Association in Bangalore on March 16, 1928. Raman proceeded to…
Read More
In his laboratory at Western Reserve University (Now Case Western Reserve University), Edward W. Morley carried out his research on the atomic weight of oxygen that provided a new standard to the science of chemistry. The accuracy of his analyses has never been superseded by chemical means. His…
Read More
Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier studied at the Académie des Sciences de l'Institut de France (then "Collège Mazarin") from 1754 to 1761. He was elected to the Royal Academy of Sciences in 1768, where he presented his important studies on oxygen in chemistry. These began with a "pli cacheté" of Nov. 2…
Read More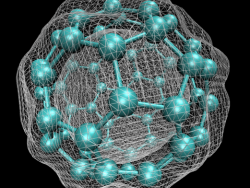
In early September 1985, a team of scientists discovered a previously unknown pure carbon molecule, C60, which they dubbed buckminsterfullerene. The name was chosen because the geodesic domes of Buckminster Fuller provided a clue that the molecule’s atoms might be arranged in the form of a…
Read More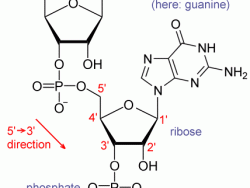
In 1961, in the National Institutes of Health Headquarters (Bethesda, MD), Marshall Nirenberg and Heinrich Matthaei discovered the key to breaking the genetic code when they conducted an experiment using a synthetic RNA chain of multiple units of uracil to instruct a chain of amino acids to add…
Read More
When Joseph Priestley discovered oxygen in 1774, he answered age-old questions of why and how things burn. An Englishman by birth, Priestley was deeply involved in politics and religion, as well as science. When his vocal support for the American and French revolutions made remaining in his…
Read More
In 1962 Neil Bartlett demonstrated the first reaction of a noble gas. The noble gas family of elements - helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon - had previously been regarded as inert. By combining xenon with a platinum fluoride, Bartlett created the first noble gas compound. This…
Read More

In 1900, Moses Gomberg, Professor of Chemistry at the University of Michigan, confirmed the existence of a stable, trivalent organic free radical: triphenylmethyl. In so doing, he challenged the then prevailing belief that carbon could have only four chemical bonds. Gomberg’s discovery made a…
Read More
In the years 1926 to 1956, the German chemist Hermann Staudinger carried out his pathbreaking research on macromolecular chemistry in Freiburg. His theories on the polymer structures of fibers and plastics and his later research on biological macromolecules formed the basis for countless modern…
Read More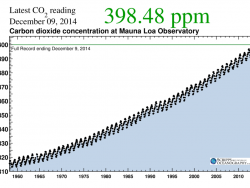
Charles David Keeling of Scripps Institution of Oceanography was the leading authority in establishing the global atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) record. In 1958, Keeling began measuring atmospheric CO2 concentrations from Hawaii’s Mauna Loa Observatory. Using rigorous analytical procedures,…
Read More
Izaak Maurits Kolthoff (1894–1993) has been described as the father of modern analytical chemistry for his research and teaching that transformed the ways by which scientists separate, identify, and quantify chemical substances. Once a collection of empirical recipes and prescriptions, the field…
Read More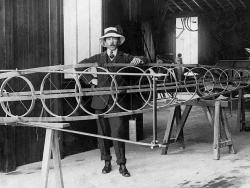
Born 20 July 1873 in the state of Sao Paolo, Alberto Santos Dumont moved to Paris in 1891 but never forgot his birthplace. He soon began experimenting with flying, and designed his first balloon, the Brasil, in 1898. He later built and flew 11 dirigibles, including the…
Read More
The first company in the United States dedicated solely to the production of the liquid rocket engine, Reaction Motors, Inc. (RMI) was formed in 1941. Its four founders were rocket enthusiasts and members of the American Rocket Society. RMI developed the rocket motors that powered…
Read More
On this site, which was the Dutch Flats Airport, Charles A. Lindbergh made the first flight of his Spirit of St. Louis airplane, constructed in 60 days by dedicated employees of Ryan Airlines, Inc. The 20-minute flight on 28 April 1927 was witnessed by those who built the aircraft.…
Read MoreT.S.C. Lowe’s Observation Flight
Thaddeus Sobieski Constantine Lowe demonstrated the use of a hydrogen-filled balloon in aerial reconnaissance through a series of tethered ascents in June, 1861 in front of…
Read More
On 4 June 1783, Joseph Michel and Jacques Etienne Montgolfier captured the imagination of the world with their first balloon flight at Cordeliers Square. There were no passengers, but the Regional Council and the whole town population saw the machine go up and stay aloft at…
Read More

