The Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) was developed at the USDA National Runoff and Soil Loss Data Center at Purdue University in a national effort led by Walter H. Wischmeier and Dwight D. Smith. The USLE was published in 1965 in USDA Agriculture Handbook 282.
1960-1969

A = average annual soil loss (in tons/acre)
R = rainfall erosivity index
K = soil erodibility factor
LS = topographic factor
C = cropping factor
P = conservation practice factor

The concept of once-over mechanical, as opposed to multiple-pick hand or experimental multiple-pick machine harvesting, represented a major break-through in the practice of producing vine fruit such as pickling cucumbers. In the 1950s the cost of hand harvesting was as high as 50% of the production cost. Once-over mechanical harvesting, coupled with increasing plant population, reduced this cost to 25% thereby making production economically viable.

Established in 1907, the American Society of Agricultural Engineers (ASAE) was managed by volunteers. In 1925, local editor Raymond Olney was named secretary, thus establishing ASAE in this area. By 1969, with over 7,000 members in 100 countries, an ASAE building was constructed at this site in St. Joseph, Mi. In 2005, ASAE became ASABE to recognize the importance of biology in the profession. ASABE collects and maintains the unique body of knowledge for the agricultural/biological engineering profession.

A crucial step in the evolution of modern plant agriculture was the development of low-cost, energy-efficient greenhouse structures that provide optimum growing conditions year-round. In 1964, Professor William J. Roberts developed the first air-inflated double-layer polyethylene greenhouse covering system at Cook College, Rutgers University.

A drive system that keeps the antenna pointed with millimeter precision regardless of factors such as environmental change
The Arecibo Observatory has the largest radio telescope ever constructed. Maintaining the greatest electromagnetic wave gathering capacity of any telescope, it has been an essential tool in modern astronomy, ionosphere and planetary studies.

Apollo astronauts who ventured outside of the protective confines of their pressurized capsules faced a number of hazards, among them: exposure to cosmic debris, solar radiation, and surface temperatures that widely varied. The suit also needed to accommodate a wide range of motion to allow the duties of the missions to be successfully accomplished.
Referred to as the "catalyst of the Industrial Revolution," textile manufacturing helped to transform the American economy from an agricultural to a manufacturing economy. It led to transitions from human to mechanical power and from wood to metal construction. Population shifts resulted from significant numbers of people moving from rural areas to work in urban factories. The collection of tools and machinery housed at the American Textile History Museum (ATHM) represents a collection of ideas which developed during this period.

On 23 November 1963, this site received the first transpacific transmission of a TV signal from Mojave earth station in California, U.S.A., via the Relay 1 communications satellite. The Ibaraki earth station used a 20m Cassegrain antenna, the first use of this type of antenna for commercial telecommunications. This event demonstrated the capability and impact of satellite communications and helped open a new era of intercontinental live TV programming relayed via satellite.

Pleumeur-BodouCountry: FranceWebsite: http://www.ieeeghn.org/wiki/index.php/Milestones:First_Transatlantic_Reception_of_a_Television_Signal_via_Satellite,_1962
On 11 July 1962 a station in Pimsleur-Bodou received the first transatlantic transmission of a TV signal from a twin station in Andover, Maine, USA via the TELSTAR satellite. The success of TELSTAR and the earth stations, the first built for active satellite communications, illustrated the potential of a future world-wide satellite system to provide communications between continents.

On the morning of 17 April 1967, radio astronomers used this radiotelescope at DRAO and a second one at the Algonquin Radio Observatory located 3074 km away to make the first successful radio astronomical observations using Very Long Baseline Interferometry. Today, VLBI networks span the globe, extend into space and continue to make significant contributions to both radio astronomy and geodesy.
Innovations

The Southwest Research Institute Split-Hopkinson Pressure Bar apparatus is a mechanical test instrument used to characterize the dynamic response of materials at high strain rates (typical of impacts and explosions).
The apparatus, based on devices invented by Bertram Hopkinson and…
Read More



The 1992 Nobel Prize in physics was awarded to Georges Charpak, France, for his invention and development of detectors in high energy physics. Since 1959 Charpak had worked at CERN, the European laboratory for particle physics situated in the canton of Geneva in Switzerland. Charpak invented the…
Read More

Operated by the Philadelphia Electric Company (PECO), now known as Exelon Corp., Eddystone Station Unit #1 is a 325 MW pulverized-coal-fired plant that pushed the technology of steam-electric generating plants. When built in 1960, engineers sought to make a more efficient plant using higher…
Read More
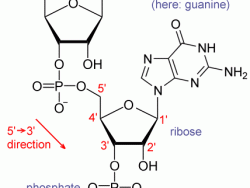
In 1961, in the National Institutes of Health Headquarters (Bethesda, MD), Marshall Nirenberg and Heinrich Matthaei discovered the key to breaking the genetic code when they conducted an experiment using a synthetic RNA chain of multiple units of uracil to instruct a chain of amino acids to add…
Read More

The Arecibo Observatory has the largest radio telescope ever constructed. Maintaining the greatest electromagnetic wave gathering capacity of any telescope, it has been an essential tool in modern astronomy, ionosphere and planetary studies. Several feats of mechanical engineering went into the…
Read More
In 1962 Neil Bartlett demonstrated the first reaction of a noble gas. The noble gas family of elements - helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon - had previously been regarded as inert. By combining xenon with a platinum fluoride, Bartlett created the first noble gas compound. This…
Read More
This machine, designed by Alton S. Newell, efficiently reduced automobile bodies into scrap metal for recycling. A body was fed into the shredder at a controlled rate, and rotating hammers, driven by a 500-hp motor, shredded it into small pieces that were easily shipped. The process took about…
Read More
The N.S. Savannah was the first nuclear-powered cargo-passenger ship, built by the New York Shipbuilding Corporation at Camden, New Jersey. The 74 maximum-power thermal megawatt pressurized-water reactor was supplied by the Babcock & Wilcox Company. Nearly 600 feet long with 22,000-tons…
Read More

The Stanford Linear Accelerator Center was renamed in 2009 to the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory.
Notable for: unique electromechanical devices and systems in the longest accelerator in the world
The Stanford two-mile accelerator, the longest in the world,…
Read More
The basic research tool at SLAC is an intense beam of electrons that have been accelerated by an electric field equivalent to 30 billion volts, making this the most powerful electron beam in the world.
The two-mile linear accelerator produces this field using high-power microwaves…
Read MoreEstablished 1965 the Tidbinbilla Tracking Station, as well as the Honeysuckle Creek (1967-1981) and Orroral Valley (1965-1985) sites, supported NASA’s Deep Space Network, Manned Space Flight Network, and Spacecraft Tracking and Data Acquisition Network. The stations played a key role in…
Read MoreEstablished 1965 the Orroral Valley Station, as well as the Honeysuckle Creek (1967) and Tidbinbilla (1965) sites supported NASA’s Deep Space Network, Manned Space Flight Network, and Spacecraft Tracking and Data Acquisition Network. The stations played a key role in supporting the Apollo 11…
Read MoreEstablished between 1967, the Honeysuckle Creek Tracking Station, along with the Tidbinbilla and Orroral Valley sites, supported NASA’s Deep Space Network, Manned Space Flight Network, and Spacecraft Tracking and Data Acquisition Network. The stations played a key role in supporting the Apollo…
Read More

