Scoates Hall 1932 A Historic Landmark of Agricultural Engineering Named for Daniels Scoates Designer of this Building Professor and Head Department of Agricultural Engineering 1919 to 1939 Eleventh President of ASAE Teacher, Writer, Engineer Counselor to Youth, His Example Still Inspires. Dedicated by the American Society of Agricultural Engineers 1978
TX

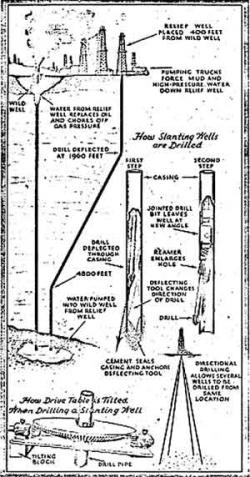
H. John Eastman introduces controlled directional drilling in 1929 and was awarded a patent the following year.
The technique became widely adopted after an oil strike in Conroe, Texas, caught fire in January 1933. The well exploded, creating a 600-foot deep crater, and the oil burned for months. Although the fire was eventually put out, oil continued to flow into the “lake.” The only way to manage this was to drill another well to relieve the pressure.

The 1940 Air Terminal is a beautiful and rare example of classic art deco airport architecture from the golden age of flight. Designed by noted architect Joseph Finger, the Terminal was built to meet Houston’s growing role as a major center for air commerce in the 1930s. Its grand opening by the City of Houston took place on September 28, 1940, at Houston Municipal Airport, now known as Hobby Airport.

When Robert G. LeTourneau started moving earth in 1919, he thought that land leveling should require only one man. In 1920, by installing a generator and electric motors, R.G. was able to control the scraper blade from the tractor seat while driving the tractor.
In June 1922, LeTourneau developed his “Mountain Mover” with a telescoping bowl. He incorporated a floor behind the cutting edge taken from his previous designs, and employed welding instead of riveting to save weight.
On 12 September 1958, Jack S. Kilby demonstrated the first working integrated circuit to managers at Texas Instruments. This was the first time electronic components were integrated onto a single substrate. This seminal device consisted of a phase shift oscillator circuit on a tiny bar of germanium measuring 7/16” by 1/16” (11.1 mm by 1.6 mm). Today, integrated circuits are the fundamental building blocks of virtually all electronic equipment.

The tower was designed to rest on a continuous reinforced concrete mat, 4 feet thick, with the base of the slab 24 feet below street level.
What makes the Texas Commerce Bank Building revolutionary in the civil engineering world is not so much the building itself, but its foundation. Initial studies for the type of foundation to be used began in the fall of 1927. William E. Simpson, the building's chief structural engineer, suggested using a mat foundation, something new for Houston's multistory buildings.

San Antonio's River Walk, a catalyst for abundant commercial and tourism enterprise, is generally regarded by cities and urban planners throughout the world as a prototype for the development of urban riverfront sites. The River Walk's success, however, would not have been possible without a series of flood-control and architecture projects completed in the first half of the 20th century that relied heavily on civil-engineering expertise.

William Emory was an 1831 graduate of the U.S. Military Academy at West Point. When the Mexican War broke out, he was assigned as chief engineer officer to General Stephen Kearny, whose army traversed largely unknown territories in the West. The U.S. War Department would later print 10,000 copies of Emory's Notes of a Military Reconnaissance, which made a significant contribution to understanding the geography and topography of the Southwest.

Historically, a camino real (Royal Road) is defined as a road that connects Spanish capital with Spanish capital, a distinction not shared with roads connecting ordinary Spanish or Indian villages. The term Camino Real implied that the status and privileges granted to the villas and capitals it connected were extended to the main routes of travel through use by officials and others acting in the interest of the crown. Unlike ordinary Indian and Spanish villages, villas like San Antonio and others along the route had charters that prescribed royal privileges.

The San Jacinto Monument commemorates the decisive 1836 battle near the banks of the Buffalo Bayou and the San Jacinto River that allowed Texas to win independence from Mexico. It is the world's tallest monument, rising 15 feet higher than the Washington Monument.
In 1936, Daughters and Sons of the Republic of Texas led lobbying efforts to allocate funds for a monument that would mark the importance of the Battle of San Jacinto. Ground was broken on April 21, 1936 - 100 years to the day after the victorious battle.
Innovations

The ABACUS II, designed and built by Texas Instruments, was the first practical automated production machine for the assembly of integrated circuits. Using heat and pressure, it bonded fine gold wire to microscopic contacts on the silicon chip and pin connections on the package.
The…
Read More
The Southwest Research Institute Split-Hopkinson Pressure Bar apparatus is a mechanical test instrument used to characterize the dynamic response of materials at high strain rates (typical of impacts and explosions).
The apparatus, based on devices invented by Bertram Hopkinson and…
Read More
The Glengyle is the earliest known survivor of the fleet of heavyweight, all-steel sleepers built by Pullman Company. The design was introduced in 1907 as a marked improvement over the wooden version then in use. Some 10,000 were built, in various configurations, the last in 1931. The Glengyle…
Read More
This is one of the earliest uses of engineered water supply and irrigation systems in the United States. The first of eight original acequias was under construction in 1718 and two are still in operation. The remains of one are visible on the grounds of the Alamo. The Acequias of San Antonio are…
Read More
In its infancy, Hangar Nine housed Curtiss JN-4s ("Jennys") like the one Charles Lindbergh landed there when he reported for duty as a flying cadet in 1924.
As the U.S. was preparing to enter World War I, the Army raced to build an entire airfield, complete with 16 wooden hangars,…
Read More


The largest rolled-earth fill dam in the world at the time of its completion, Denison Dam eventually served as a prototype for dam construction in future U.S. Army Corps of Engineers projects throughout the arid plains of the American Southwest. Procedures and equipment developed during…

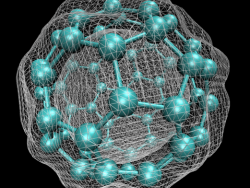
In early September 1985, a team of scientists discovered a previously unknown pure carbon molecule, C60, which they dubbed buckminsterfullerene. The name was chosen because the geodesic domes of Buckminster Fuller provided a clue that the molecule’s atoms might be arranged in the form of a…
Read More
Galveston Island is a barrier island located two miles off the Texas coast. The island is about 3 miles wide at its widest and about 28 miles long. The Galveston Seawall extends over 10 miles along Galveston's oceanfront, protecting life and property against hurricanes and tropical storms. …
Read More
On April 21, 1949, a completely outdoor turbine-generator was placed into commercial operation at the Greens Bayou electric power plant--the first fully outdoor unit to operate in the United States. The demand for unprecedented quantities of electricity after World War II pressed utilities to…
Read More
This is an old technology brought here by new immigrants. It represents the beginning of modern life in a hard wilderness. This wind-powered gristmill was built in 1870 by Fred Meiss, Jr., and Otto Fiek near Spring Creek, from parts of the first windmill in the new state of Texas, erected by E.G…
Read More
The terminal, designed by noted architect Joseph Finger and built by the Works Progress Administration, is a rare remaining example of classic art deco airport architecture, featuring the distinctive design elements of that age: step forms, sweeping curves, and intricate geometrical patterns and…
Read More
The 50-mile Houston Ship Channel is a manmade port for ocean-going vessels, stretching from the Gulf of Mexico to Houston and Harris County, Texas.
The waterway was originally known as Buffalo Bayou and was swampy, marshy, and overgrown with dense vegetation. Steamboats and…

Prior to 1909 the traditional fishtail bit scraped the rock and quickly dulled in service. The Hughes two-cone bit's revolutionary rolling action crushed hard-rock formations with twin cone-shaped, hardened steel bits, each with 166 cutting edges, revolving on bronze bearings shaped to provide a…
Read More
This machine, designed by Alton S. Newell, efficiently reduced automobile bodies into scrap metal for recycling. A body was fed into the shredder at a controlled rate, and rotating hammers, driven by a 500-hp motor, shredded it into small pieces that were easily shipped. The process took about…
Read More

The San Jacinto Monument commemorates the decisive 1836 battle near the banks of the Buffalo Bayou and the San Jacinto River that allowed Texas to win independence from Mexico. It is the world's tallest monument, rising 15 feet higher than the Washington Monument.
In 1936, Daughters and…
Read More
Historically, a camino real (Royal Road) is defined as a road that connects Spanish capital with Spanish capital, a distinction not shared with roads connecting ordinary Spanish or Indian villages. The term Camino Real implied that the status and privileges granted to the villas and capitals it…
Read More

